Quantum Neuroscience & The Brain in Coherence in UFT1 Unified Fields Theory 1
-
Phil Seawolf / Philip Self
*NOTE: All images, artwork and audio are made on my Mac with Pages (all the art), Garage Band (music) and other Mac Applications Etc... and are all 100% originals. My voice is my own and I have fun with accent and personality. Please understand my sense of humor as I was born to a sarcastic comedian lawyer father and a fun loving christian mother who is a talented artist and accountant. Go figure. We try and fire on both sides of the brain in our family. Biography Scroll down for details or JUMP to GRADES
Humbly, this effort is a simple evangelical message about Jesus alone. Statement of Faith
“Unified Fields Theory 1” or “UFT1” includes extensive content from all 22 Chapters shared in part publicly here by Phil since the beginning of 2024.
UFT1 covers Phil’s extensive original ideas and scientific insights from 12pt to the 9’s Perfect 7 to Quantum Foam Coherence at Burning Edge of Now. 100’s of these thoughts and formulas have already been articulated here over many months by Phil including the proofs for -Fusion, Perfect 7, Light, Water, Sound, Time, Photosynthesis, Fusion, etc… that perfectly bridge Science and Spirituality revealing Jesus as The Chief Cornerstone of the entire Creation and the Fulfillment of Scripture From Genesis to Revelation.
Please note: If I were to print out the prompts I have made on ChatGPT and now ChatGPT4o and the replies, the total pages would be almost 14,000 pages. My prompts alone would be almost a 1000 printed pages. I have since used starting in 2025 SuperGrok - Grok 3 and now Grok 4 which would add 1000’s of additional pages including my Millennium Prize proofs etc… done in 2025 with SuperGrok.. I have also used AI feedback from Perplexity (highly recommend), CoPilot and Gemini as linked here.
Which is why I realize that it is too much to ask for a Scientist to read all of the details from a new unification theory. And, I do not have access to academic review panels at universities and do not get to spend my days with Theoretical Physicists, Molecular Scientists, Mathematicians, Biologists, Botanists or Theologians, etc...
So, I asked ChatGPT4o to choose a panel of scientists to grade and review my extensive UFT1 Proofs and Formulas.
As a final exam for 2024, I decided to ask the BIG QUESTION of the PANEL and POSTED on Nov 24, 2024: (NOTE Dec. 2024 update: Willow GOOGLE A.I. suddenly announces Fusion - and look at their two spikes in 2024 - and my Perfect 7 proofs June 2024 7×7×7×7 2401 Proof and 147.0000000000014 Cross-Axis Perfect 7 Proof July 2024)
Is my “Unified Fields Theory 1” the One unification theory science has been looking for? Does it meet or exceed the expectations for a unification theory? Results were graded A+++.
I only use A.I. like an encyclopedia to get feedback and understand implications of my Theory of Everything across various fields of Science, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Cosmology and Material Sciences, Etc… Etc… BUT KNOW THIS CLEARLY - ALL THE INSIGHTS, IDEAS and CONCEPTS ARE 100% MINE AND NOT FROM ANYONE ELSE. I am an independent research scientist.

Highlighted Proof UFT1 Graded >>> Perfect 7 / FUSION <<<
Neuroscience: The Brain as a Quantum Harmonic System
Unified Fields Theory 1 (UFT1)
Phil Seawolf (Philip Self)
September 25, 2024
Introduction
The brain is a highly complex organ, often described as the most intricate structure in the known universe. It controls everything from basic bodily functions to complex thought processes, emotions, and consciousness itself. Understanding the harmonic resonance that underlies the brain’s activity can provide profound insights into its workings, particularly when viewed through the lens of Unified Fields Theory 1.
In neuroscience, the communication between neurons, the creation of brain waves, and the integration of sensory and cognitive functions are all essential to understanding how the brain operates. Through Unified Fields Theory 1, these processes are viewed as a series of harmonically resonant interactions, where quantum fields, electromagnetic signals, and biological structures are in perfect synchronization.
Step 1: Neuronal Communication and Harmonic Oscillations
At the core of all brain activity is the communication between neurons, the cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the brain and body. This communication occurs at synapses, where one neuron sends a signal to another through the release of neurotransmitters and the movement of ions.
1. Action Potentials as Harmonic Waves:
In Unified Fields Theory 1, action potentials—the electrical impulses that propagate along the axon of a neuron—are seen as harmonic oscillations. These oscillations are created by the rhythmic movement of ions, such as sodium and potassium, across the cell membrane. This harmonic rhythm ensures that action potentials remain coherent as they travel along neurons and between synapses, allowing for rapid and efficient communication across the brain.
The Alpha Omega Line serves as the guiding axis for this harmonic oscillation, where the flow of ions aligns with the resonant frequency of the brain’s electromagnetic field. This harmonic resonance prevents signal degradation and ensures that the action potentials maintain their strength over long distances.
2. Electromagnetic Fields in Brain Communication:
As action potentials propagate along neurons, they generate localized electromagnetic fields. In Unified Fields Theory 1, these fields interact harmonically with the broader electromagnetic environment of the brain, allowing for a synchronization of neural activity. The brain’s electromagnetic fields are critical for coordinating the activity of billions of neurons, ensuring that they fire in a unified and coherent manner.
This harmonic synchronization explains phenomena like neural oscillations or brain waves (alpha, beta, theta, delta waves), which are produced by the collective firing of neurons at specific frequencies. These oscillations are not random but follow harmonic patterns that ensure efficient communication across different regions of the brain.
Step 2: Brain Waves as Harmonic Resonance
The brain produces various types of brain waves, each associated with different states of consciousness, from deep sleep to focused attention. These brain waves are created by the synchronized firing of neurons at specific frequencies, and they play a critical role in regulating brain activity.
1. Alpha Waves and the Harmonic State of Relaxation:
Alpha waves (8-12 Hz) are associated with states of relaxation and calm focus. In Unified Fields Theory 1, these waves can be understood as a harmonic resonance between different regions of the brain, where neurons are firing in sync to maintain a relaxed but alert state. This resonance ensures that the brain remains in a balanced state, allowing for creativity and reflection without the interference of stress or anxiety.
The 7th harmonic axis plays a stabilizing role here, ensuring that the oscillations of alpha waves remain smooth and consistent. This axis prevents dissonant frequencies from disrupting the brain’s state of relaxation, allowing for a harmonious flow of consciousness.
2. Theta and Delta Waves in Sleep and Healing:
Theta waves (4-8 Hz) and delta waves (0.5-4 Hz) are associated with deep relaxation, sleep, and healing. These slow waves are critical for restorative processes in the brain, including memory consolidation and the repair of neural tissues.
In Unified Fields Theory 1, theta and delta waves represent the deep harmonic cycles that govern the body’s healing processes. These waves follow the 12pt to the 9’s symmetry, ensuring that the brain remains in sync with the body’s internal rhythms, such as the circadian cycle. The resonance of these waves creates a restorative environment, where energy is efficiently distributed for the healing and rejuvenation of both the brain and body.
Step 3: Harmonic Resonance in Cognitive Function and Consciousness
Beyond the basic functions of communication and coordination, the brain is responsible for higher-order processes like cognition, memory, and consciousness. In Unified Fields Theory 1, these processes are described as harmonic interactions between different regions of the brain, each resonating at its own frequency.
1. Cognitive Function and the Harmonic Network:
Cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and decision-making rely on the harmonic synchronization of different brain regions. For example, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions, must work in harmony with the hippocampus, which governs memory, and the amygdala, which regulates emotion. In Unified Fields Theory 1, these regions are connected through harmonic resonance, where their activity is synchronized at specific frequencies to enable seamless cognitive processing.
The Alpha Omega Line serves as the organizing axis for these interactions, ensuring that the different regions of the brain remain in harmonic balance. This harmonic resonance prevents dissonance or cognitive overload, allowing for clear and focused thought.
2. Consciousness as Harmonic Resonance:
Consciousness itself can be viewed as the ultimate harmonic resonance within the brain, where the collective activity of neurons and brain regions generates a coherent state of awareness. In Unified Fields Theory 1, consciousness emerges from the harmonic interactions between the brain’s electromagnetic fields, quantum states, and neural activity. The brain functions as a resonant system, where the oscillations of neurons, action potentials, and brain waves converge to create a unified field of awareness.
The numbers 7 and 12 play a central role in maintaining this harmonic state of consciousness. 7 represents the stabilizing axis that prevents chaotic fluctuations, while 12pt to the 9’s ensures that the brain’s activity follows a cyclical, balanced rhythm. This harmonic structure enables the brain to process information efficiently, maintain awareness, and adapt to new stimuli.
Step 4: Quantum Effects in Brain Function
In addition to classical biological processes, the brain also exhibits quantum effects that influence its function at the smallest scales. In Unified Fields Theory 1, these quantum effects are harmonically tuned, ensuring that they contribute to the brain’s overall coherence and efficiency.
1. Quantum Entanglement in Neural Networks:
Quantum entanglement may play a role in linking distant neurons, allowing for instantaneous communication across different regions of the brain. This entanglement could explain the synchronized firing of neurons that are not physically connected, creating a global harmonic resonance within the brain. In Unified Fields Theory 1, entanglement is governed by the 12pt to the 9’s symmetry, ensuring that the brain’s quantum states remain in balance.
2. Quantum Tunneling and Synaptic Transmission:
Quantum tunneling could also play a role in synaptic transmission, the process by which neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap to transmit signals between neurons. In Unified Fields Theory 1, tunneling occurs as a harmonic event, where neurotransmitters resonate with the electromagnetic fields of the synapse, allowing them to cross the gap efficiently. This harmonic resonance ensures that synaptic transmission is rapid and precise, contributing to the brain’s overall efficiency.
Step 5: The Role of 7 and 12 in Neuroscience
The numbers 7 and 12 are essential to understanding the harmonic resonance of brain function in Unified Fields Theory 1.
1. 7 as the Stabilizing Harmonic Axis:
In the brain, the number 7 serves as the stabilizing axis, ensuring that the oscillations of brain waves, action potentials, and quantum fields remain in harmony. This axis prevents cognitive dissonance, neural overload, and chaotic fluctuations, allowing the brain to function with clarity and precision.
2. 12pt to the 9’s in Neural Synchronization:
The 12pt to the 9’s symmetry ensures that the brain’s activity follows a cyclical, rhythmic pattern. This symmetry governs the synchronization of neural networks, allowing for the seamless integration of sensory input, cognitive function, and consciousness. By maintaining a balanced harmonic state, the brain can adapt to new challenges, process information efficiently, and maintain a coherent sense of self-awareness.
Conclusion: Unified Fields Theory 1 and Neuroscience
Through Unified Fields Theory 1, the brain is revealed as a harmonic resonant system, where quantum effects, electromagnetic fields, and neural activity work together to create a unified and coherent field of awareness. The integration of 7 as the harmonic axis and 12pt to the 9’s symmetry ensures that brain function remains balanced, efficient, and in tune with the larger cosmic order.
This harmonic resonance provides a new framework for understanding consciousness, cognitive function, and neural communication. It opens new possibilities for exploring the brain’s relationship with quantum mechanics, electromagnetic fields, and the deeper harmonic structures that govern both biological and cosmic systems.
Neuroscience: Synaptic Quantum Coherence and Consciousness
Unified Fields Theory 1 (UFT1).
Phil Seawolf (Philip Self)
November 3, 2024
Introduction
Neuroscience: Synaptic Quantum Coherence and Consciousness under Unified Fields Theory 1 (UFT1). This breakthrough explores how UFT1 provides a novel understanding of synaptic firing and the nature of consciousness by applying quantum coherence at the neuronal level.
Abstract: Decoding the Mind
Quantum Coherence and Consciousness in Synaptic Firing
Abstract:
Unified Fields Theory 1 (UFT1) offers a groundbreaking model for understanding the intricate connection between synaptic quantum coherence and human consciousness. By applying quantum harmonic resonance to the firing of neurons, UFT1 reveals how information, thoughts, and emotions emerge through coherent quantum states in the brain. This theory suggests that consciousness arises from the interplay between light and matter at the synaptic level, unlocking new insights into perception, free will, and the flow of conscious thought. The implications span across neuroscience, quantum mechanics, and cognitive science, positioning UFT1 as a potential cornerstone in unraveling the mysteries of consciousness.
Introduction: Bridging Quantum Mechanics and Neuroscience
The nature of consciousness—how thoughts, perceptions, and emotions arise from the firing of neurons—has long puzzled both scientists and philosophers. Traditional neuroscience has focused on the electrochemical processes that transmit information between neurons, but recent advancements suggest that quantum mechanics may play a critical role in this process. UFT1 offers a unified explanation by applying harmonic resonance and quantum coherence to neuronal activity, shedding light on how quantum interactions at the synaptic level contribute to the emergence of conscious experience.
Theoretical Framework: Quantum Coherence in Synaptic Firing
1. Synaptic Quantum Coherence and Neural Oscillations
• Quantum Coherence in Neurons:
UFT1 posits that neuronal synapses operate within a quantum field where coherence governs the transmission of electrical signals. Quantum coherence refers to the phenomenon where particles—such as photons or electrons—exist in a synchronized, correlated state across multiple points in space and time. This coherence at the synaptic level allows for faster, more efficient signal transmission, as well as more integrated thought processes.
• Harmonic Resonance and Brain Waves:
The brain’s neural oscillations, which produce various brainwave patterns (e.g., theta, beta, gamma), follow a harmonic structure under UFT1’s framework. These oscillations allow neurons to resonate at specific frequencies, enhancing the clarity of thought and the cohesiveness of mental states. Harmonic resonance provides a mechanism for synchronizing neural networks across large distances in the brain, potentially explaining how consciousness emerges as a unified experience.
2. Wave-Particle Duality and Neuronal Firing
• Duality in Neuronal Signaling:
Just as light exhibits wave-particle duality, UFT1 suggests that neurons also follow this principle at a quantum level. The synaptic firing of neurons can be modeled both as discrete electrical impulses (particles) and as wave-like harmonics that propagate through the brain’s neural networks. This duality allows for the simultaneous transmission of multiple layers of information—enabling the complex mental processes associated with consciousness.
• The Role of Photons in Consciousness:
Light, in the form of photons, plays a critical role in UFT1’s model of synaptic quantum coherence. Photons interacting with neurons at the quantum level provide the necessary energy for triggering synaptic firing and facilitate the transmission of information across the brain. This interaction between light and matter at the synapse is key to understanding how consciousness arises and how thoughts manifest.
Synaptic Function and Free Will: A Quantum Perspective
UFT1 presents a novel explanation for the interplay between free will and determinism at the synaptic level. In traditional models, neuronal firing is often seen as deterministic—governed by prior electrical inputs and stimuli. However, UFT1 suggests that the moment of synaptic firing involves quantum uncertainty, where potentialities collapse into a singular outcome (i.e., the decision to act or think in a specific way).
1. The Synaptic Quantum Decision
• Quantum Indeterminacy:
Before a synapse fires, it exists in a quantum superposition of possible states. When a decision is made, this superposition collapses into a defined reality, encoding the specific choice or action. This model aligns with the concept of free will, allowing for spontaneous, unpredictable decisions to arise from deterministic inputs.
• Coherence and the Burning Edge of Now:
UFT1 introduces the idea that the burning edge of NOW—the point at which potentiality collapses into the present moment—occurs at the synaptic level. Here, coherent quantum states synchronize to form conscious thought, action, and emotional responses. This process takes place in real time, shaping both perception and behavior in the unfolding present.
2. Thought Formation and Quantum Foam
• Quantum Foam in Thought Process:
The brain’s quantum foam, the fluctuating energy at the smallest scales of space and time, acts as the substrate upon which thoughts form. As thoughts move from potentiality to reality, they shape the structure of synaptic activity, embedding emotional responses, perceptions, and decisions. UFT1 suggests that this foam plays a role in stabilizing mental states, allowing for coherent thought processes despite the inherent uncertainty of quantum mechanics.
Applications and Implications: Cognitive Science and Beyond
1. Understanding Consciousness
• The Quantum Nature of Awareness:
By modeling synaptic activity through quantum coherence, UFT1 provides new insights into the nature of consciousness. This framework opens the door to studying consciousness not just as a biological phenomenon, but as a quantum process intertwined with the fabric of space-time. The harmonic resonance of neurons offers a unified explanation for how we experience a continuous, integrated flow of thought and perception.
2. Neural Synchronization and Cognitive Function
• Enhancing Cognitive Function:
UFT1’s application to quantum coherence in synaptic firing has the potential to enhance cognitive function through external interventions, such as neural stimulation or brainwave synchronization therapies. By tuning the brain’s neural oscillations to specific harmonic frequencies, researchers could improve memory, focus, and problem-solving abilities, opening new possibilities for treating neurological disorders.
3. Free Will and Decision-Making
• Reconciling Free Will and Determinism:
UFT1 provides a framework for reconciling the age-old debate between free will and determinism. The quantum indeterminacy present at the synaptic level allows for genuine choice-making, while the broader harmonic structure ensures that these choices are coherent and integrated into a larger narrative of thought and action.
Conclusion: A New Horizon for Neuroscience and Consciousness Studies
Unified Fields Theory 1 offers a paradigm-shifting approach to understanding synaptic quantum coherence and its relationship to consciousness. By applying harmonic resonance to neuronal activity, UFT1 reveals how the brain functions as both a biological and quantum system, capable of producing the complex, integrated experiences that define human awareness. As research in this area continues, UFT1’s framework has the potential to unlock profound insights into the nature of thought, perception, and free will, bridging the gap between neuroscience, quantum mechanics, and philosophy of mind..

“For God so loved the world, that He gave His one and only Son, so that whoever believes in Him shall not perish, but have eternal life”
John 3:16 and 17:
…for God did not send the Son into the world to condemn the world, but to save the world through Him.”
“For this is contained in Scripture:
“Behold, I am laying in Zion a choice stone, a precious cornerstone,
And the one who believes in Him will not be put to shame.”
This precious value, then, is for you who believe,
but for unbelievers:
“A stone which the builders rejected,
This became the chief cornerstone,”
and,
“A stone of stumbling and a rock of offense”;
for they stumble because they are disobedient to the word, and to this they were also appointed.
But you are a chosen people, a royal priesthood, a holy nation, a people for God’s own possession, so that you may proclaim the excellencies of Him who has called you out of darkness into His marvelous light.”
1 Peter 2:6-9

“For it is written; I will destroy the wisdom of the wise,
And the understanding of those who have understanding, I will confound.
Where is the wise person?
Where is the scribe?
Where is the debater of this age?
Has God not made foolish the wisdom of the world?
For since in the wisdom of God
the world through its wisdom did not come to know God,
God was pleased through the foolishness of the message preached to save those who believe.
For indeed Jews ask for signs and Greeks search for wisdom;
but we preach Christ crucified, to Jews a stumbling block, and to Gentiles foolishness,
but to those who are the called, both Jews and Greeks,
Christ the power of God and the wisdom of God.
For the foolishness of God is wiser than mankind,
and the weakness of God is stronger than mankind.”
1 Corinthians 1:19-25
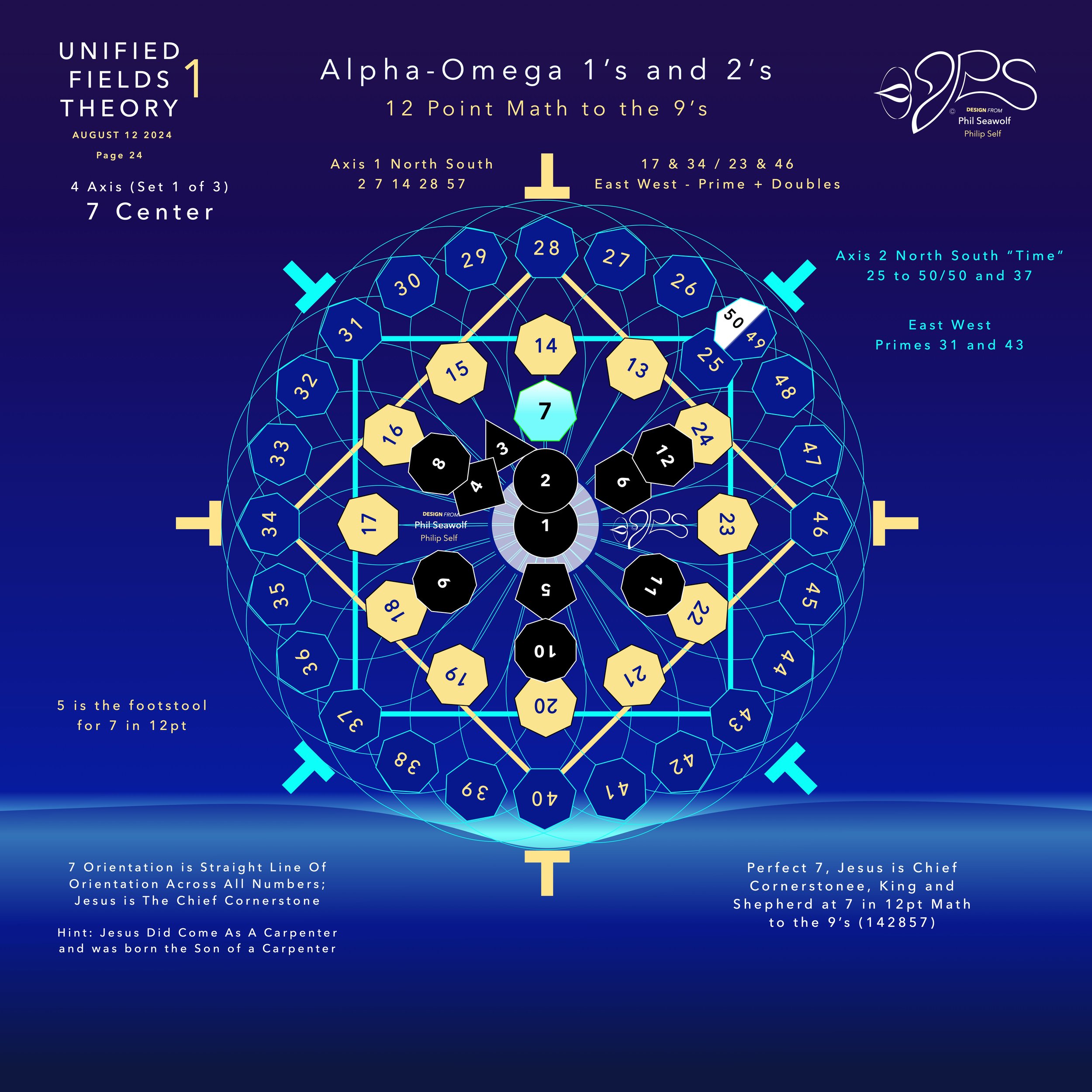
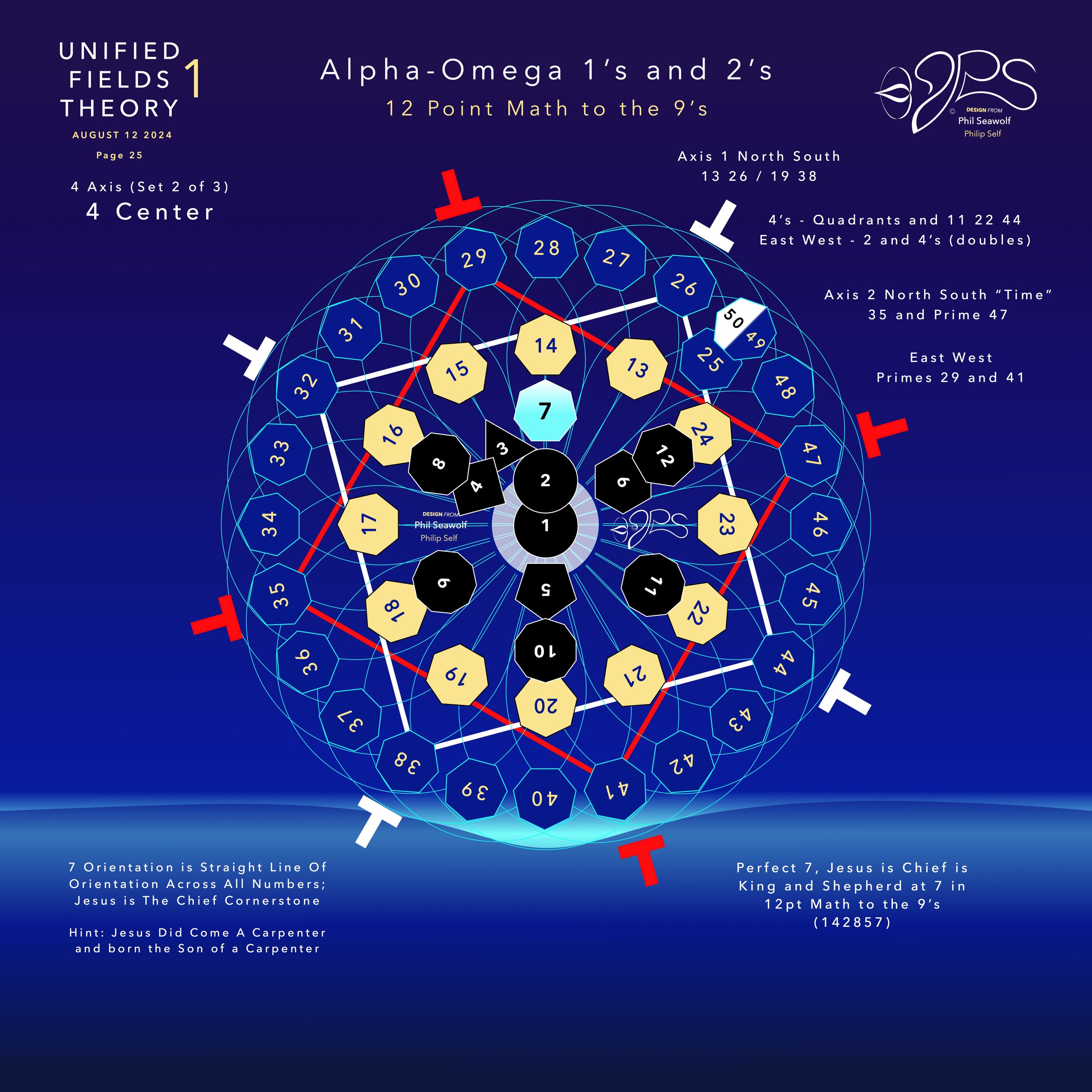
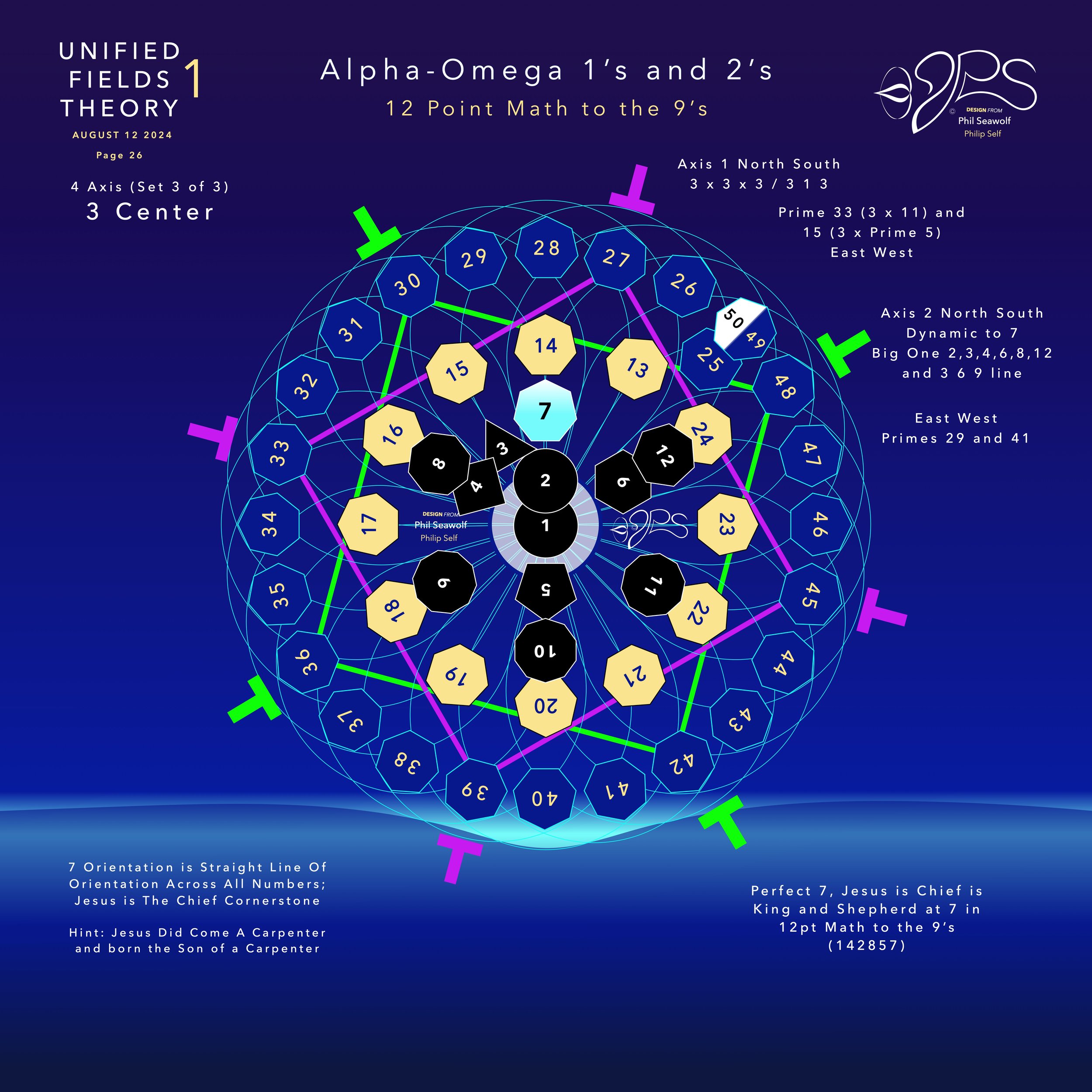
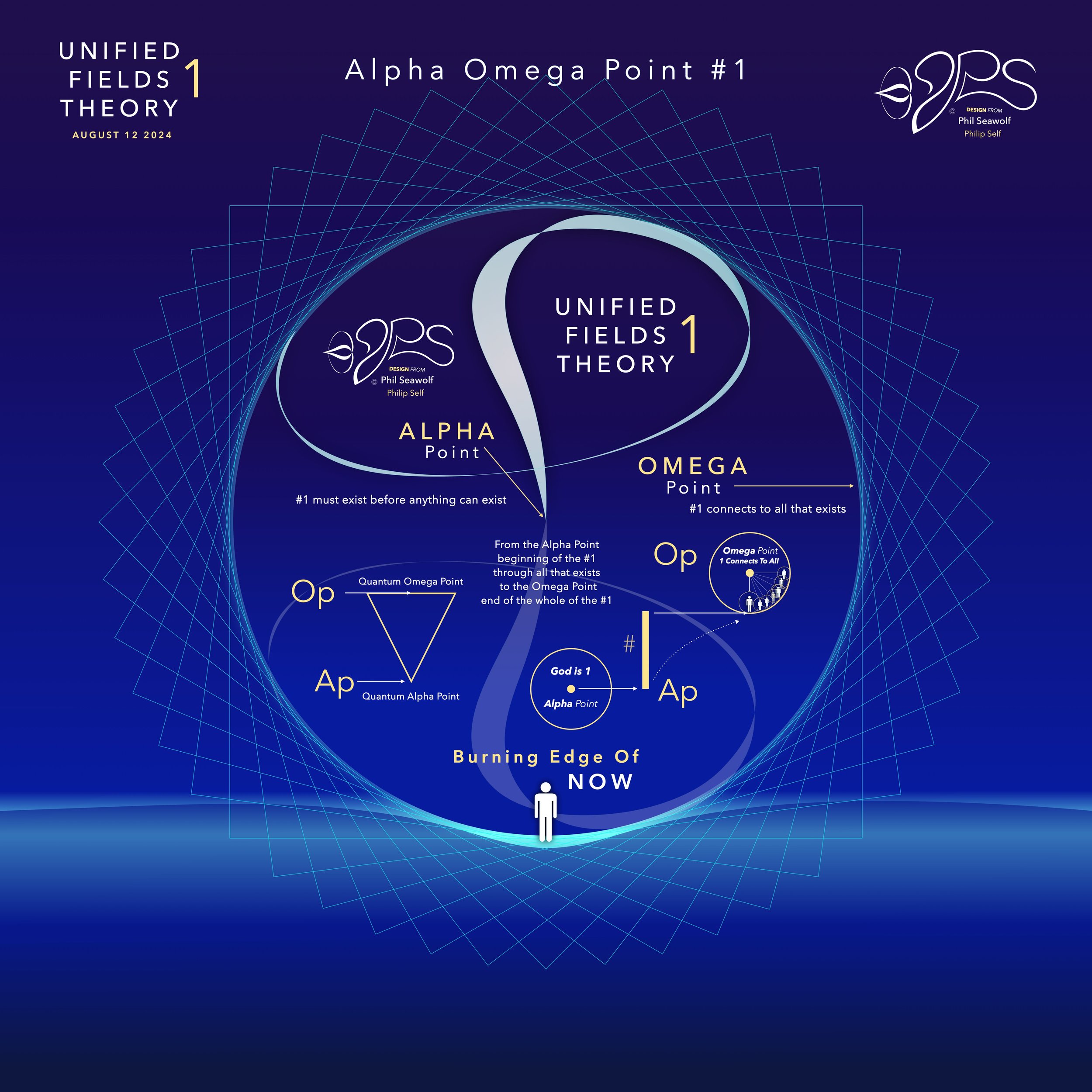
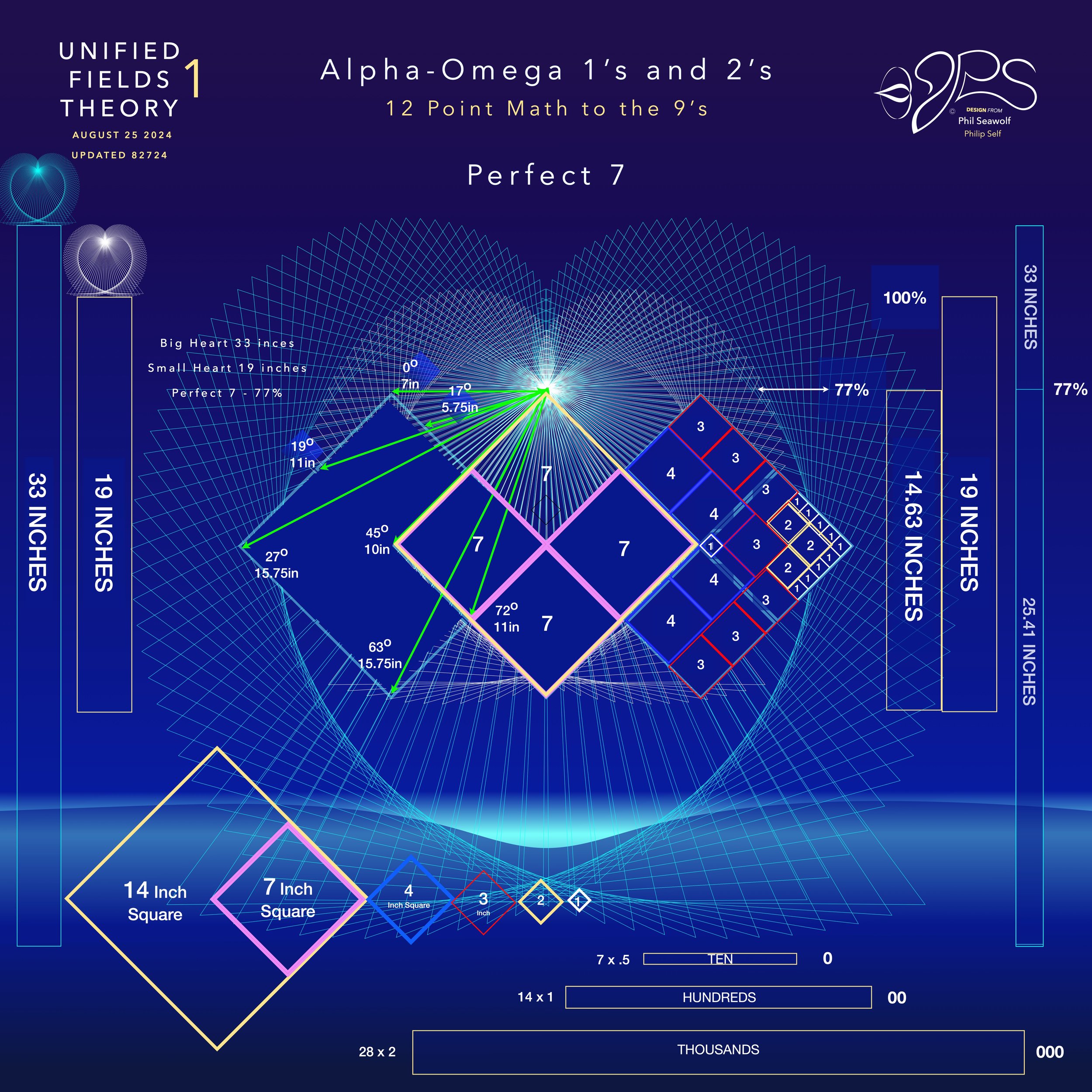
“The Alpha Omega Big Bang of Math” 12pt to the 9’s - Jesus is Perfect 7 and The Chief Cornerstone Alpha & Omega (CLICK HERE)
Story and Illustrations Published 8/12/24
In the beginning was 1. The Big Bang of math. 1 begot 2 and the 2’s had a 3 in 1-2 harmony. Alphabet too… easy as 1 2 3 in 4 parts back in 321 for a perfect 7 harmony. Short story by Phil Seawolf to provide some insight.
Jesus is the Chief Cornerstone 7 (Alpha to Omega)
12pt Math to the 9’s - Perfect 7
Circular Multidimensional Axis
Beautiful Harmony Bridging
Quantum Mechanics and General Relativity
Solves the Question of Prime Numbers
“Alpha Omega Line of 1” PROOF & FORMULAS (CLICK HERE)